Defining the four C's, cut, clarity, color, and carat weight and explaining diamond certification, grading reports, and appraisals.
The appearance of a diamond depends more on its cut than any other characteristic. The brilliance of a diamond is produced from light entering the top of the diamond, reflecting off the facets, and dispersing back through the top of the diamond.
1. A diamond that has "ideal cut" proportions has been cut to a mathematically proven proportion to produce the ultimate in brilliance.
2. A diamond that has been cut with too much depth will lose light out the side of the pavilion of the diamond.
3. A diamond that has been cut too shallow will lose light through the bottom of the diamond.
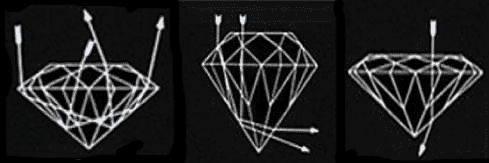

The ideal cut diamond has been cut to perfect proportions for the ultimate in brilliance. The symmetry of an ideal cut diamond is shown in the graph below.

The clarity characteristics of a diamond are classified as inclusions or blemishes. A diamond's inclusions are its identifying marks and distinguish it from other diamonds. Clarity grading is achieved using a 10X microscope or jewelers loupe.
 |
Diamonds come in many colors with the majority being sold in the range of colorless to faint yellow. The most widely used color scale was developed by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA). The GIA scale begins at D (colorless) and runs to Z (light yellow).
Colorless: D-E-F. The highest color grade for diamond is no color. A colorless diamond allows white light to pass through it and the light disperses as a rainbow of colors.
Near colorless: G-H-I-J. Visually, in the near colorless range of G-H-I, the diamond shows no noticeable color to the eye. At J color you can detect a slight color to the diamond.
Faint yellow to very light yellow: K through Z. Visibly yellow color to the diamond.
 |
| Colorless | Near Colorless | Faint Yellow | Very Light Yellow | Light Yellow | Fancy |
| D E F | G H I J | K L M | N O P Q R | S-Z | Yellow |
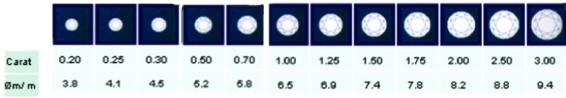
The weight of a diamond is measured in carats. One carat is equal to 100 points, three quarter carat is equal to .75 points, half carat is equal to .50 points, etc. Weighing the carat weight of a diamond on a diamond scale is the easiest determination of the four C's.
A diamond certification is a report created by a gemologist after measuring the diamond's weight and reviewing the diamond under a microscope for color, clarity, symmetry, and finish grading. Each diamond is issued its own certification number and report.
The diamond grading laboratories most well known and respected are the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), the American Gem Society (AGS), and the European Gemological Laboratory (EGL). There are also many independent gemological laboratories that follow the strict grading procedures of GIA and AGS.
All loose diamonds purchased at Swissa Jewelers will come with certification.
A jewelry appraisal will accompany each piece of jewelry purchased from Swissa. The appraisal will state the replacement cost for the item purchased. It is the responsibility of each customer to forward the appraisal to your insurance company to cover loss, theft or damage to the jewelry. Swissa cannot be held liable for the loss, theft or damage of your jewelry.
Grading reports and appraisals are subjective. Each laboratory appraiser or trained jewelry appraiser may vary slightly in the scientific method used in the grading of jewelry.
With each loose diamond purchased from Swissa you will receive a laboratory grading report from either the American Gem Society (AGS), The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) or the European Gemological Laboratory (EGL). A laboratory report identifies the individual characteristics of the diamond including carat weight, color, clarity, and proportion grading. Each certificate is numbered from the diamond lab where it was certified. Purchasing a lab certified stone ensures that you are receiving the diamond you paid for, which instills more confidence for our customers.